NAME
cat-v - visualize non-printing characters
SYNOPSIS
cat-v [ options ] args ...
OPTIONS
-n --reset Disable all character conversion
-c --visible=# Specify visualize characters
--repeat=# Specify repeat characters
-t --expand[=#] Expand tabs
-T --no-expand Do not expand tabs
--ts --tabstyle=# Set tab style
--tabstop=# Set tab width
--tabhead=# Set tab-head character
--tabspace=# Set tab-space character
-h --help Print this message
-v --version Print version
OPTIONS FOR EACH CHARACTERS
--esc Enable escape
--esc=c Show escape in control format
--esc=+c Show escape in control format and reproduce
--nl=0 Disable newline
--sp=~ Convert spaces to tilde
--sp='OPEN BOX' Unicode name
--esc=+U+035B Unicode code pointVERSION
Version 0.9902
DESCRIPTION
The cat -v command is often used to display characters that cannot be displayed, but is not always suitable for viewing the output of modern applications because it converts all non-ASCII characters.
The cat-v command visualizes whitespace and control characters while preserving the display of displayable graphic characters.
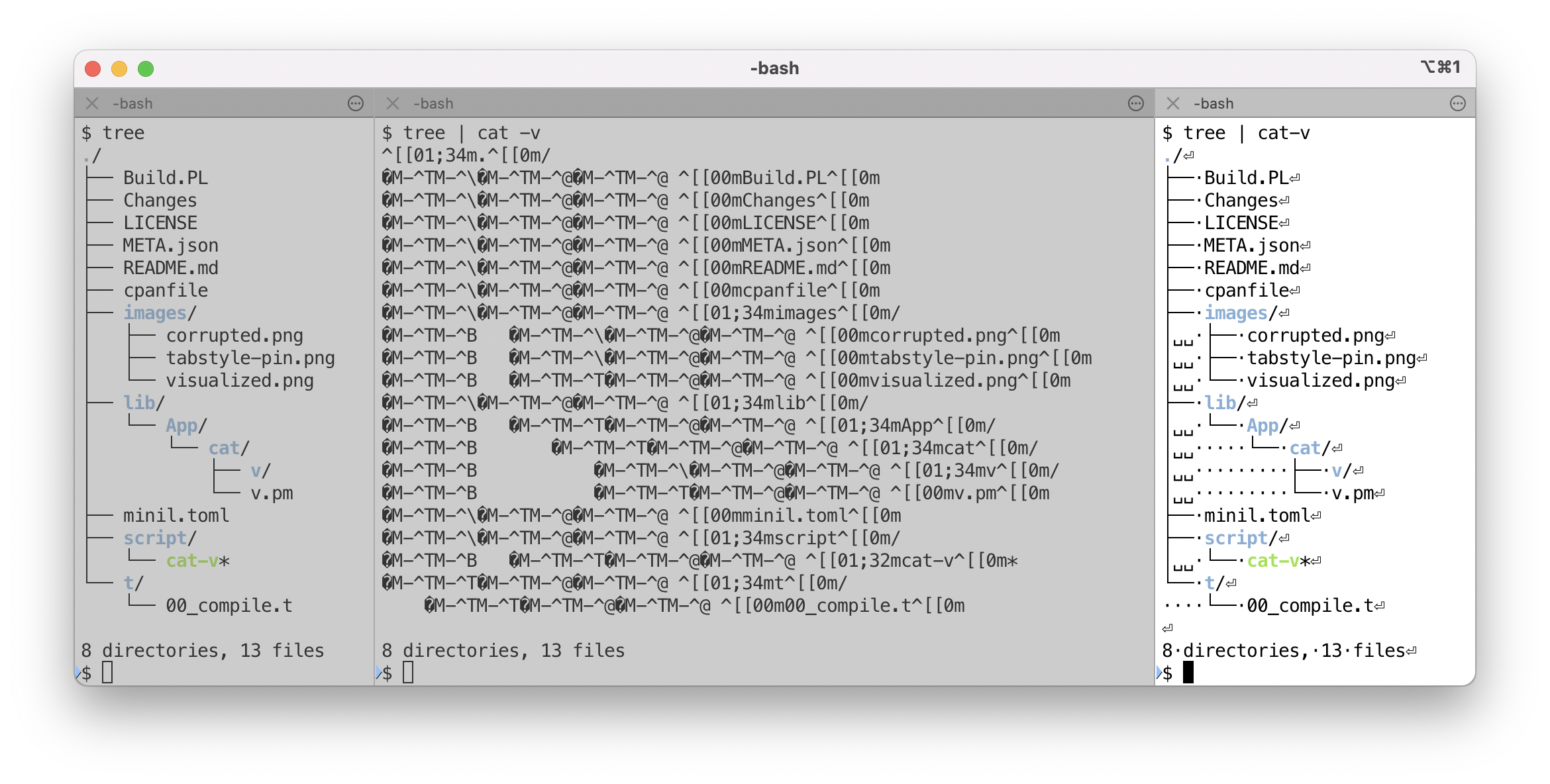
Also, by default, escape characters are not converted, so decorations by ANSI escape sequences are retained.
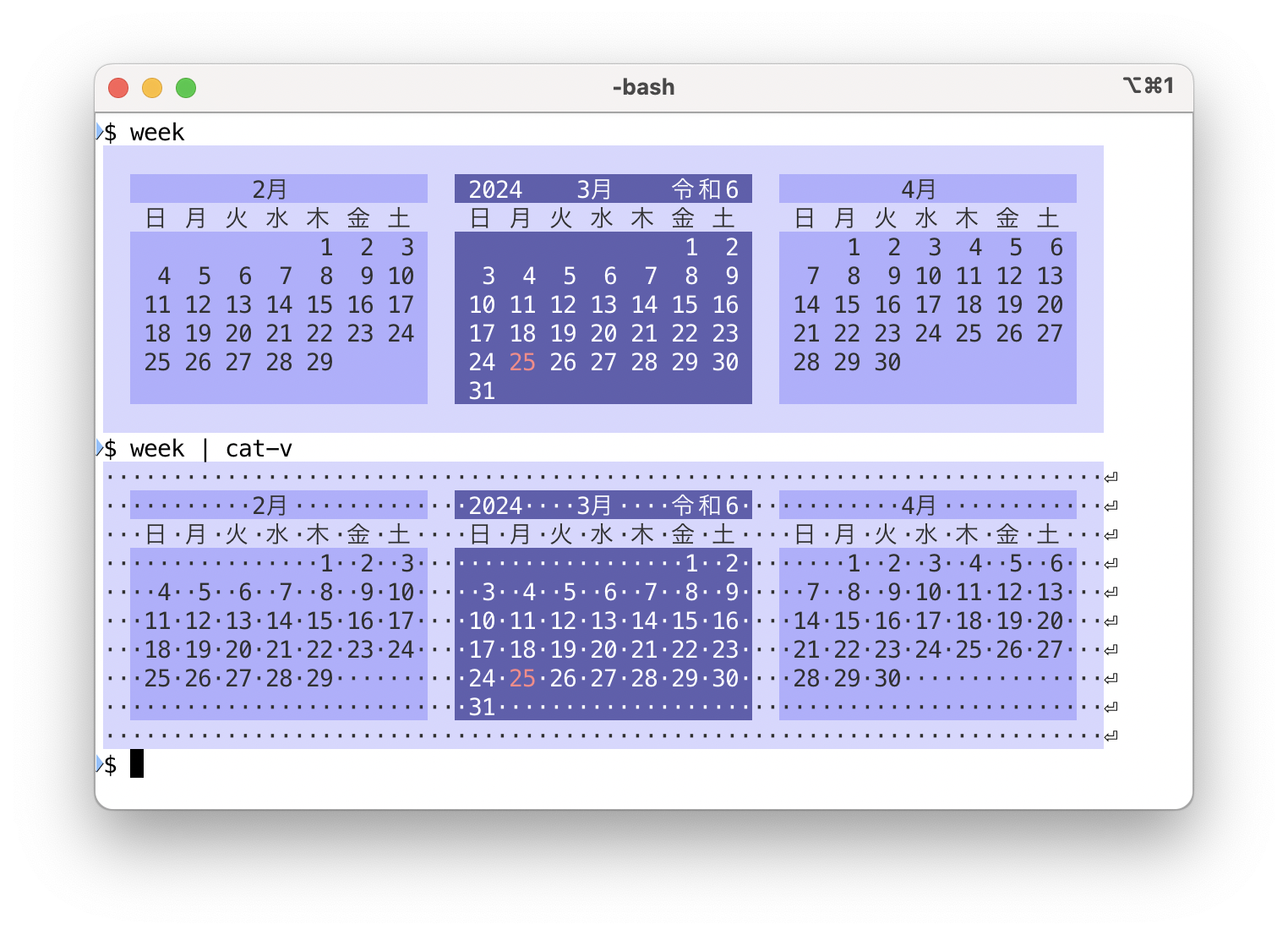
Sometimes it is desirable to visualize whitespace characters. The cat -t command can visualize tab characters, but the problem is that it breaks the visual format. We may want to see which parts are tabs and which parts are space characters while preserving the format. Extra whitespace characters at the end of a line can also be noticed by visualizing them.
Using cat-v, tab characters are visualized in such a way that the space on the display does not change.

Control characters can be displayed in control format and Unicode symbol characters. By default, control characters other than newline and escape characters are displayed as corresponding Unicode symbols.
The second field is the default action. s stands for symbol, m for Unicode mark, and 0 for no conversion.
nul s \000 \x{2400} ␀ SYMBOL FOR NULL
soh s \001 \x{2401} ␁ SYMBOL FOR START OF HEADING
stx s \002 \x{2402} ␂ SYMBOL FOR START OF TEXT
etx s \003 \x{2403} ␃ SYMBOL FOR END OF TEXT
eot s \004 \x{2404} ␄ SYMBOL FOR END OF TRANSMISSION
enq s \005 \x{2405} ␅ SYMBOL FOR ENQUIRY
ack s \006 \x{2406} ␆ SYMBOL FOR ACKNOWLEDGE
bel s \007 \x{2407} ␇ SYMBOL FOR BELL
bs s \010 \x{2408} ␈ SYMBOL FOR BACKSPACE
ht s \011 \x{2409} ␉ SYMBOL FOR HORIZONTAL TABULATION
nl m \012 \x{240A} ␊ SYMBOL FOR LINE FEED
vt s \013 \x{240B} ␋ SYMBOL FOR VERTICAL TABULATION
np m \014 \x{240C} ␌ SYMBOL FOR FORM FEED
cr s \015 \x{240D} ␍ SYMBOL FOR CARRIAGE RETURN
so s \016 \x{240E} ␎ SYMBOL FOR SHIFT OUT
si s \017 \x{240F} ␏ SYMBOL FOR SHIFT IN
dle s \020 \x{2410} ␐ SYMBOL FOR DATA LINK ESCAPE
dc1 s \021 \x{2411} ␑ SYMBOL FOR DEVICE CONTROL ONE
dc2 s \022 \x{2412} ␒ SYMBOL FOR DEVICE CONTROL TWO
dc3 s \023 \x{2413} ␓ SYMBOL FOR DEVICE CONTROL THREE
dc4 s \024 \x{2414} ␔ SYMBOL FOR DEVICE CONTROL FOUR
nak s \025 \x{2415} ␕ SYMBOL FOR NEGATIVE ACKNOWLEDGE
syn s \026 \x{2416} ␖ SYMBOL FOR SYNCHRONOUS IDLE
etb s \027 \x{2417} ␗ SYMBOL FOR END OF TRANSMISSION BLOCK
can s \030 \x{2418} ␘ SYMBOL FOR CANCEL
em s \031 \x{2419} ␙ SYMBOL FOR END OF MEDIUM
sub s \032 \x{241A} ␚ SYMBOL FOR SUBSTITUTE
esc 0 \033 \x{241B} ␛ SYMBOL FOR ESCAPE
fs s \034 \x{241C} ␜ SYMBOL FOR FILE SEPARATOR
gs s \035 \x{241D} ␝ SYMBOL FOR GROUP SEPARATOR
rs s \036 \x{241E} ␞ SYMBOL FOR RECORD SEPARATOR
us s \037 \x{241F} ␟ SYMBOL FOR UNIT SEPARATOR
sp m \040 \x{2420} ␠ SYMBOL FOR SPACE
del s \177 \x{2421} ␡ SYMBOL FOR DELETE
nbsp s \240 \x{2423} ␣ OPEN BOXAt this time, Unicode markings are available for the following characters
nul \x{2205} ∅ EMPTY SET
bel \x{237E} ⍾ BELL SYMBOL
nl \x{23CE} ⏎ RETURN SYMBOL
np \x{2398} ⎘ NEXT PAGE
sp \x{00B7} · MIDDLE DOTOPTIONS
- -n, --reset
-
Disables all character conversions and resets repeat characters.
- -c, --visible name=flag,...
-
Give the character type and flags as parameters to specify the character to be visualized and the conversion format.
c control style s symbol style m Unicode mark (if exists) 0 do not convert * non-alphanumeric char is used as a replacementOption
-c nl=1can also be used to visualize newline characters. For newline characters only, after displaying the result of the conversion, the original character is output at the same time.Use the names in the list above to specify by character type. If you want to convert escapes without converting tabs, use the following
cat-v -c tab=0 -c esc=sMultiple items can be specified at the same time. The following example sets
tabandbelto 0 andesctos.cat-v -c tab=bel=0,esc=sIf
allis specified for the name, the value applies to all character types. The following command sets all characters tos, then setsnl,nl,np, andsptomand disablesesc. This is the default state.cat-v -c all=s,nul=nl=np=sp=m,esc=0 - --name[=replacement]
-
All control characters can also be accessed by an option with their name. For example, option
--nlis defined for the newline character.Used alone, it activates the visibility of the character.
cat-v --nlTo disable, give the value 0.
cat-v --nl=0If a letter other than an alphabet or a number is given, it will be replaced by that letter.
cat-v --nl='$'If a string of two or more characters is given, it is interpreted as a Unicode character name.
cat-v --nl='RETURN SYMBOL' --sp='MIDDLE DOT'If flag begins with
+, that character is added to the repeat list.cat -v --esc=+sSo the above command will have the same meaning as if you had written as following.
cat -v --esc=s --repeat +esc - --repeat=name[,name...]
-
Specifies the character type for outputting the original character at the same time as the converted character. The default setting is
nl,np. The following will correctly output the original ANSI sequence with the escape character visualized.cat-v -c esc --repeat esc,nlIf name begins with
+, add that character in addition to the existing configuration.cat-v -c esc --repeat +esc - -t[n], --expand[=n]
- -T, --no-expand
-
Tab characters are expanded by default. To explicitly disable it, use the -T or --no-expand option.
If an optional number is given for the -t option, it is treated as a tab width. The following two commands are equivalent:
cat-v -t4 cat-v -t --tabstop=4By default, the style
pinis applied, which can be changed with--tabstyle. If the--tabstyleoption is specified with no arguments, a list of available styles is displayed.You can disable tab expansion by default by putting the following setting in your
~/.cat-vrcfile.option default --no-expandIn such cases, tab expansion can be temporarily enabled by the
-toption. - --tabstop=# (DEFAULT: 8)
-
Set tab width.
- --tabhead=#
- --tabspace=#
-
Set tab head and following space characters. If the option value is longer than single character, it is evaluated as unicode name.
- --tabstyle, --ts
- --tabstyle=style, --ts=...
- --tabstyle=head-style,space-style --ts=...
-
Set the style how tab is expanded. Select
symbolorshadefor example. If two style names are combined, likesquat-arrow,middle-dot, usesquat-arrowfor tabhead andmiddle-dotfor tabspace.Show available style list if called without parameter. Styles are defined in Text::ANSI::Fold library.
INSTALL
CPANMINUS
From CPAN archive:
cpanm App::cat::vFrom GIT repository:
cpanm https://github.com/tecolicom/App-cat-v.gitSEE ALSO
- https://github.com/tecolicom/App-cat-v.git
-
Git repository.
- App::optex::util::filter
-
The predecessor of the
cat-vcommand was originally created as the filter module of the App::optex command.
AUTHOR
Kazumasa Utashiro
LICENSE
Copyright © 2024 Kazumasa Utashiro.
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the same terms as Perl itself.